PHYSICS: WAVE
What is wave?
Waves is the vibration that travels through an object from one place to another or a wave can be described as a disturbance that travels through a medium from one location to another location.
There are 2 types of waves:
1. Transverse Waves
Transverse waves happen on a rope or on water. Transverse waves are always in a form of a peak and a valley of the wave. The height of the peak and the valley is considered as the amplitude of the wave. A complete wave is always consists of one peak and one valley of the wave. A complete wave is called a wave-length.
2. Longitudinal Waves
Transverse waves happen on a rope or on water. Transverse waves are always in a form of a peak and a valley of the wave. The height of the peak and the valley is considered as the amplitude of the wave. A complete wave is always consists of one peak and one valley of the wave. A complete wave is called a wave-length.
2. Longitudinal Waves
Longitudinal waves are waves that have a compression part and a expansion part, instead of a peak or valley. A complete wave of a longitudinal wave consists of one compression part and one expansion part. The length of a longitudinal wave is equal to the length of a wave that consists of a compression part and a expansion part.
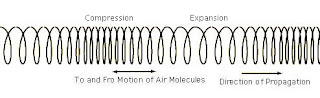 |
| An example of longitudinal waves. You can see a compression and a expansion every wave. |
Examples:
1 complete wave = a - b - c - d - e
It consists one peak (a) and one valley (c)
A to B = 1/4
A to C = 1/2
A to D = 3/4
A to E = 1 wave
A to H = 1 3/4 wave
A to G = 1 1/2 wave
B to C = 1/4 wave
B to E = 3/4 wave





